Profile
From flows of money between banks or ideas among scientists to pandemic outbreaks and range shifts of species, Martin Rosvall’s research focuses on developing methods for revealing the inner workings of interconnected systems to answer questions in various areas of science.
Martin was born in Uppsala and grew up north of Umeå. He went to a high school for cross-country skiing in Lycksele before his undergraduate in engineering physics. After his Ph.D. in network science at the Niels Bohr Institute in Copenhagen, Martin moved to the Department of Biology at the University of Washington in Seattle for his postdoc. There he started working on a grand challenge in network science: how to simplify and highlight essential regularities in networks into maps. Mapping networks is a holy grail of data science because in the myriad links and nodes of a network hide answers to how we can predict how the system will evolve.
From 2009 at Umeå University, Martin has continued to develop and integrate new math, algorithms, and visualizations into powerful mapping tools for efficiently going from interaction data to insightful maps, new hypotheses, and unexpected discoveries. With a thriving research group in IceLab and a growing collaboration network, the applications now extend across both the natural and social sciences.
As a professional power napper, Martin’s favorite place in IceLab after lunch is a hidden couch.
Martin lives between the university and the ski trails with his wife Marie Halén and their two daughters born in 2014 and 2018. When he is not playing with his family, you will find him increasing his dopamine levels on cross-country skis.
In 2014 Martin received the Nordea Science Prize and in 2018 the Young Scientist Award for Socio- and Econophysics.
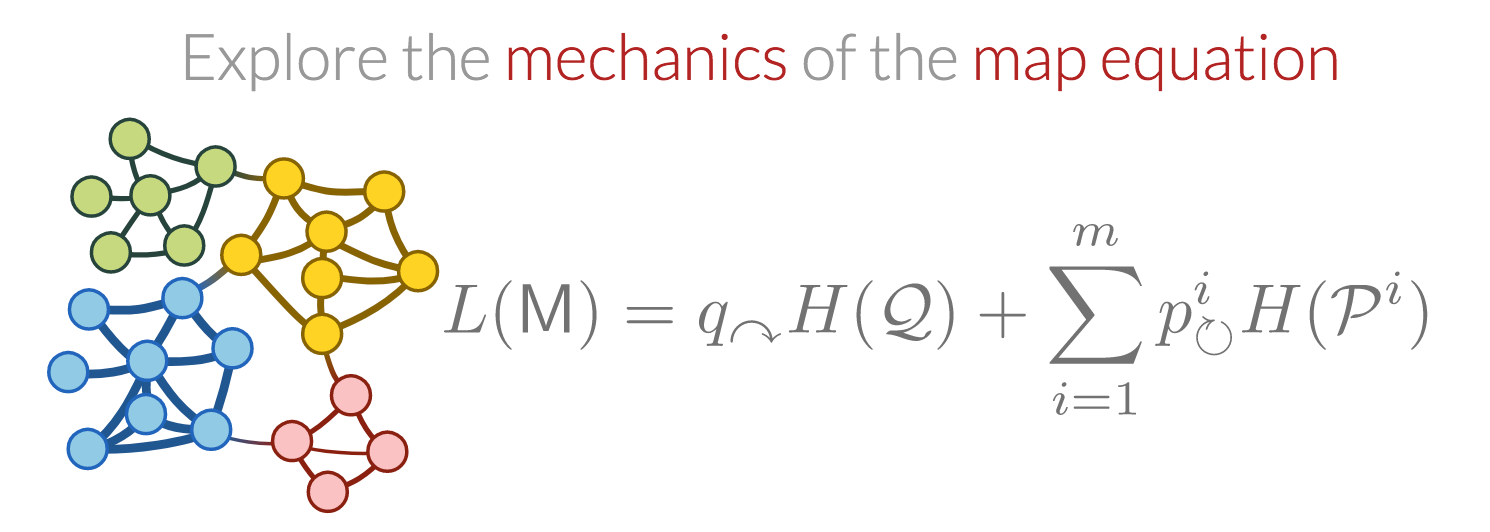
Map Equation
Martin Rosvall’s site MapEquation.org houses a number of applications based on the map equation.
Infobaleen
Martin Rosvall is a co-founder of the university spin-off Infobaleen. For the many organizations struggling to understand and use their data, Infobaleen develops flexible tools that help them go from data to insights and valuable actions.
The Latest Posts
Check out the latest updates by this IceLabber here